Product Manuals
Download user manuals, instructions and brochures for our products all in one place!
Can't find what your looking for?
Fill the form below to let us know which product manual you need and we will do our best to make it available.
Let us know
Sleep Manuals
Click Here to visit our Sleep Solutions website
Home Oxygen
-
Equipment User Guide
Download the document PDF (56.35 MB)
Portable Oxygen Concentrators
Inogen
-
Inogen G3 - User Manual
Download the document PDF (1.92 MB) -
Inogen G4 - User Manual
Download the document PDF (3.25 MB) -
Inogen G4 - Technical Manual
Download the document PDF (342.07 KB) -
Inogen G5 - User Manual
Download the document PDF (1.64 MB) -
Inogen Rove 6
Download the document PDF (16.97 MB)
Philips
-
Simply Go - User Manual
Download the document PDF (3 MB) -
Simply Go - Quick Start Guide
Download the document PDF (1.78 MB) -
Simply Go - Spec Sheet
Download the document PDF (236.27 KB) -
Simply Go Mini - User Manual
Download the document PDF (7.62 MB) -
Simply Go Mini - Brochure
Download the document PDF (330.35 KB)
Transportable Oxygen Concentrators
-
Eclipse 5
Download the document PDF (17.22 MB) -
Zen-O
Download the document PDF (1.49 MB)
Stationary Oxygen Concentrators
Devilbiss
-
Devilbiss 10L
Download the document PDF (2.38 MB) -
Devilbiss 5L
Download the document PDF (3.81 MB)
Philips
-
Everflo - User Manual
Download the document PDF (1.48 MB) -
Everflo - Brochure
Download the document PDF (962.15 KB)
Invacare
-
Perfecto V - User Manual
Download the document PDF (1.6 MB) -
Perfecto V - Brochure
Download the document PDF (3.27 MB) -
Perfecto 2
Download the document PDF (1.61 MB) -
Platinum 9L - User Manual
Download the document PDF (947.1 KB) -
Platinum 9L - Service Manual
Download the document PDF (3.49 MB)
Oscillating Positive Expiratory Pressure (OPEP)
Aerobika
-
Aerobika - User Manual
Download the document PDF (1.09 MB) -
Aerobika - Instructions For Use
-
Aerobika - Care Instructions
Download the document PDF (902.96 KB) -
Aerobika with Manometer
Download the document PDF (1.15 MB)
AeroEclipse - Breath Actuated Nebulizer
-
AeroEclipse - User Manual
Download the document PDF (1.23 MB) -
AeroEclipse - Instructions For Use
Download the document PDF (1.78 MB)
Aerosol Compressor
-
Best Neb - Instructions
Download the document PDF (419.3 KB)
Suction
-
Aspira Go
Download the document PDF (1.76 MB) -
Du-O-Vac - Instructions
-
Twin-O-Vac - Instructions
Download the document PDF (145.13 KB)
Regulators
-
NOVA 40
Download the document PDF (91.3 KB) -
NOVA 40 - Technical Data Sheet
Download the document PDF (84.33 KB) -
Gloor Regulator
Download the document PDF (427.18 KB) -
0 Series Comweld
Download the document PDF (419.27 KB) -
SMT
Download the document PDF (816.15 KB) -
Alpinox - User Manual
Download the document PDF (1.17 MB) -
Alpinox - Instructions
Download the document PDF (607.22 KB) -
Medireg - Paediatric Regulator
Download the document PDF (1.11 MB)
Oxygen Conserving Device
-
Chad Evolution - Instructions for use
Download the document PDF (623.8 KB) -
Chad Lotus
Download the document PDF (318.53 KB) -
OCD Troubleshooting Guide
Download the document PDF (208.4 KB)
Oxygen Consumables
-
Oxymizer Pendant
Download the document PDF (668.8 KB) -
Firesafe Valve
Download the document PDF (518.52 KB) -
Firesafe Valve - FAQ
Download the document PDF (196.62 KB)
On Demand Valve
-
Sabre Ease II
Download the document PDF (4.62 MB)
Frequently Asked Questions
How is the oxygen in my blood measured?
| Your physician will confirm if the amount of oxygen in your blood is low by performing one or both of the following tests: | |
|
Arterial Blood Gas: A small amount of blood is taken from an artery (usually in the wrist). this test is very accurate and measures the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. Pulse Oximetry: A pulse oximeter is a device with a sensor that attaches to your finger to estimate how saturated your blood is with oxygen. This test is simple and pain free and will verify whether your blood levels are too low. With your physicians’ approval, Air Liquide Healthcare can perform pulse oximetry testing in the comfort of your home. |
What does my oxygen prescription mean?
Our bodies cannot store oxygen.
Your physician has prescribed oxygen therapy adapted to meet your needs.
If you decrease the use of your oxygen, the benefits will be reduced or disappear.
Your physician will prescribe the:
- Flow rate: this is the amount of extra oxygen your body will need. Your physician may want your flow rate to always be the same or you may need to change the flow rate for different activities such as resting, sleeping or exercising. Your flow rate is expressed in litres per minute (Lpm).
- Duration of use: this refers to the number of hours per day in which you should use your oxygen therapy. usually, 16 - 24 hours of use per day is required for your therapy to be effective. Your physician will advise you of your needs.
- Type of oxygen supply equipment to use: Your physician will recommend different supply systems based on funding and what is available to enhance your lifestyle. Air Liquide Healthcare can assist you with your choice of equipment from our broad range of oxygen supply systems.
Oxygen therapy prescription examples:
1) Use oxygen for at least 16 hours per day at 2 litres per minute (Lpm)
OR
2) Use oxygen for 16 hours per day at:
- 3 Lpm when sleeping
- 2 Lpm when resting
- 3 Lpm on exertion
Contact your prescribing physician if you feel that the prescribed flow of oxygen is not meeting your needs.
What equipment is used to supply home oxygen therapy?
Your physician will decide whether you require oxygen at home and/or when you leave the house.
Air Liquide Healthcare will help you select the equipment that best suits your needs.
Oxygen can be provided through three main supply systems. These systems may be used alone or indifferent combinations.
Systems include:
- Stationary oxygen concentrators
- Portable oxygen concentrators
- Oxygen cylinder
Stationary Concentrator
An oxygen concentrator is an electrically driven device that extracts the oxygen from room air.
This means that the concentrator never runs out of oxygen and never needs to be refilled. Most stationary oxygen concentrators weigh anywhere between 18 – 30 kg and cannot be used outside of the home.
Stationary oxygen concentrators feature oxygen sensing devices that will warn you if the purity of the oxygen delivered decreases, so that you can use an alternative oxygen supply system and contact Air Liquide Healthcare for assistance.
Portable Concentrator
Portable oxygen concentrators (poc) operate in a similar way to stationary oxygen concentrators but are designed to be used while you are outside of the home. The weight of portable oxygen concentrators varies between models, ranging from 2 - 8kg. As a general rule, heavier pocs are capable of delivering higher oxygen flow rates. The battery duration for portable oxygen concentrators varies between models. Batteries are recharged from your mains power at home, and most have connections to recharge from your vehicle. Your poc should be serviced regularly to ensure that it is working properly and that the oxygen purity stays within the manufacturer’s recommendations. Since the amount of oxygen produced varies greatly between models, you will need to be tested on the specific device you intend to use to ensure that it will meet your oxygen needs.
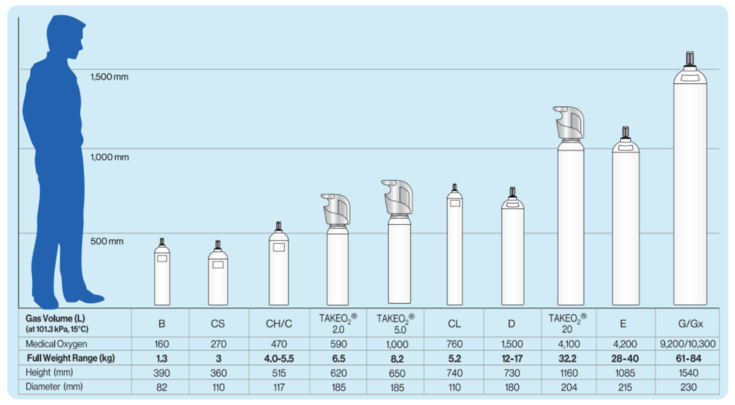
What are oxygen cylinders?
Oxygen cylinders contain oxygen in gas form. they are filled under pressure to contain a greater volume of gas. The pressure is released with the use of a regulator which is also used to set the prescribed flow rate.
Cylinders can also be used with an oxygen conserving device which only delivers a flow of oxygen when you breathe in. your cylinder will last much longer since there is no oxygen flowing when you breathe out.
Oxygen cylinders are available in a variety of sizes and are separated into two main groups; portable and stationary.
Portable (small) cylinders are lightweight cylinders used outside of the home, and are available in a variety of sizes. Smaller models are contained in a bag which can be carried over your shoulder or used as a backpack.
The larger models can be transported using a trolley. Stationary (large) cylinders are normally used as a safety ‘back up’ for stationary oxygen concentrators in the event of power failure or equipment malfunction.
They are available in a variety of sizes. selection is based on your prescribed flow rate and how far away you live from an Air Liquide Healthcare office.
What accessories do I need with my oxygen therapy?
Oxygen is typically delivered from the supply system to your nose with a ‘cannula’. extension tubes are available in a variety of lengths (up to 15 metres) to allow you to move about the house while connected to your oxygen supply system. Both the cannula and the extension
tubing are available in a variety of sizes and lengths. Based on your prescription, Air Liquide Healthcare will assist you in choosing accessories.
Firesafe cannula valves* can be connected to your oxygen accessories to provide an extra line of defence, that can limit the impact of an oxygen fire by automatically arresting the oxygen flow in the event of a fire.
Other specialty accessories are available as prescribed by your physician.
How often do I replace my oxygen accessories?
Your cannula will become dirty and brittle with use and may hurt your ears and skin if not replaced at least once to twice a month.
Extension tubing is disposable and should be replaced every three to six months to ensure that no leaks occur.
The firesafe valve is typically replaced every six months.
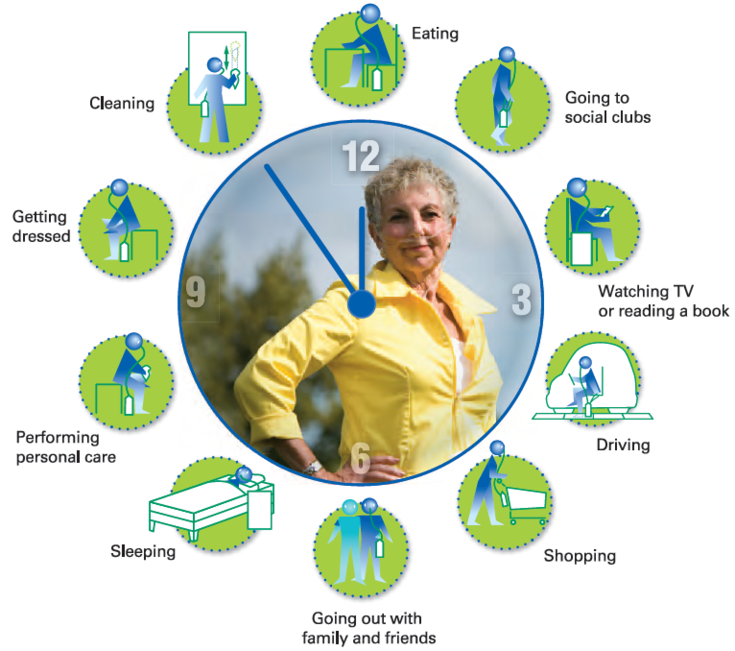
How do I use oxygen in my everyday life?
Integrating oxygen therapy into your daily routine will not only prolong your life but enhance your quality of life 1,2
Remember that the objective of using oxygen therapy is to increase the amount of oxygen in your blood, supplying enough to all organs during rest and during physical activities.
Use your oxygen as prescribed while you go about your normal routine such as running errands, doing housework, watching television or reading a book. It is important to use your oxygen even when outside of the home.
Use oxygen as prescribed in your everyday life, when:
What can I do if my ears or nose are sore?
If your nose becomes dry or sore you can use a product such as Nozoil, which is safe to use with oxygen therapy. You should never use any petroleum based products (such as creams and oils) with oxygen.
If your ears are sore, you may want to try a product such as eZ Wraps - soft foam tubes that fit over the cannula. They provide a soft cushioning for the sensitive tissue around your ears.
If you are experiencing discomfort from your oxygen therapy contact Air Liquide Healthcare for assistance.
Learn More - About our range of oxygen consumables
Shop Now - Visit our online store to purchase these products
Are there any support groups for people on oxygen therapy?
Support groups offer an opportunity to network, learn and share skills to help in a range of issues associated with health problems such as feeling low, irritability, isolation and confusion. There is also a strong focus on how to stay healthy and active.
There are a variety of established support groups including support from your area health service and Lung foundation Australia. for information on a lung support group nearest you, please contact your local healthcare facility or Lung foundation Australia:
http://lungfoundation.com.au/patient-area/patientsupport/
Our partner's safety data sheets
If you need information on medical gas properties and/or safety, health, storage, handling and emergency recommendations please refer to the following Safety Data Sheets (SDS).